A verified ISO of Wells Fargo Bank, Paynada Credit Card Processing is a Texas-based merchant account reseller headquartered in Plano. Initially operating as TranzVia since 2018, the company is an industry-leading credit card processor offering innovative solutions for clients to boost their profits and reduce overhead costs. It resells its merchant accounts through Fiserv and facilitates credit card processing with low processing charges. Read ahead for Paynada credit card processing review for their rates, complaints, and lawsuits.
Credit cards are one of the preferred means of paying for goods, but this means of payment demands a high price. The main goal behind establishing Paynada was to relieve consumers of the exorbitant processing charges for accepting credit cards. The provider facilitates affordable rates and convenient solutions to ease the burden by helping small to medium-sized businesses expand their reach.
The payment facilitator caters to all business types, including e-commerce, retail, high-risk enterprises, B2B, and hospitality. It aims to provide the necessary facilities to all clients regardless of their company’s size and requirements. Its tech-savvy equipment and highly optimized payment solutions are available to ensure profits for all. Here is a detailed Paynada Credit Card Processing review for merchants to get an idea about what to expect from the company as their payment service provider;
Paynada Credit Card Processing Review: Features and Services
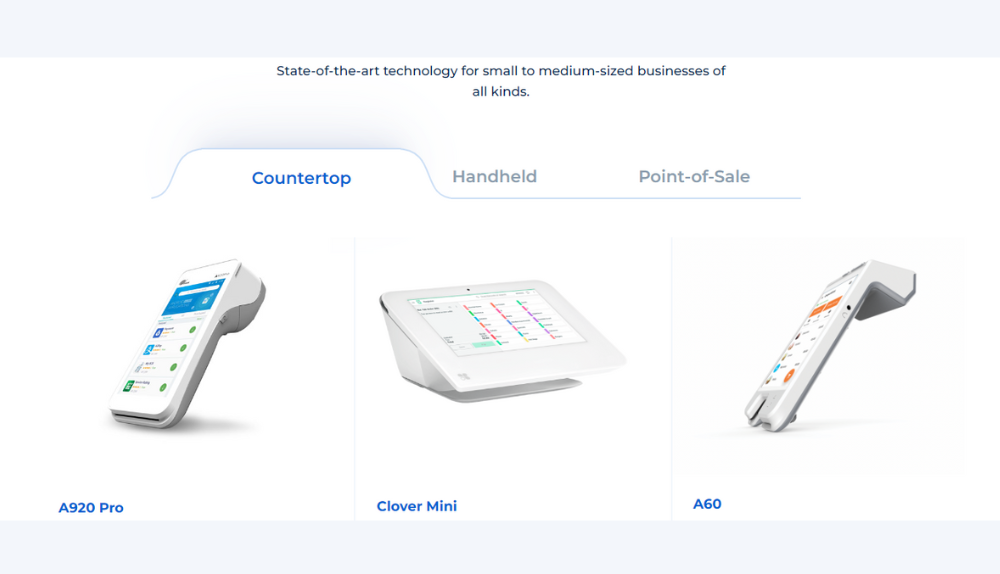
Merchants can accept all major credit cards and benefit from Paynada’s next-day funding and cash advance facilities. They can utilize the company’s handheld and countertop terminals and choose from a range of complete POS systems through Clover or PAX. The processor also offers mobile and e-commerce payment solutions to accommodate clients in all aspects.
Prioritizing data security for merchants and their customers, Paynada purveys PCI-compliant technology to ensure the authenticity of every transaction. Here is an overview of the products offered to Paynada clients;
POS System
Consumers can access the company’s proprietary POS system, MPOS, or request an E700, E800, or Clover Station Due to match their needs. Connectable through Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, these POS have HD touch screens with NFC contactless payment facility. Highly recommended for restaurants, retail stores, and hospitality businesses, the POS comes with an electronic cash register and is compatible with multiple third-party apps. Customers can get digital receipts and access features for order confirmation, tips, and rewards.
Credit Card Terminals
According to Paynada Credit Card Processing reviews, consumers are offered efficient handheld and countertop terminals to accommodate multiple payment types. They can access inventory tracking and payroll management feature and a built-in receipt printer to enhance productivity. Mobile businesses are provided with a pocket-sized card reader and wireless connectivity to accept payments on the go. Users can track sales, avail of the pay-at-the-table facility, and manage deliveries on one device.
E-Commerce Payment Solutions
The provider offers tailored solutions for e-commerce businesses, allowing them the convenience of reaching more clients on multiple platforms. Paynada Credit Card Processing reviews indicate that its seamless integrations enable consumers to effortlessly handle their web presence and provide a secure checkout experience to their customers across all channels. Users can accept electronic checks through an efficient payment gateway. Moreover, the company’s interchange optimization lowers the credit card processing cost for B2B businesses.
Security Features
All services are PCI DSS compliant to ensure additional security for businesses. The company utilized advanced technology features such as tokenization and end-to-end encryption to protect sensitive information. This lowers the chances of credit card fraud, especially in online transactions. During a data breach, it also ensures that the customer’s card information is not leaked and cannot be misused.
Paynada Credit Card Processing Review: Rates and Contract
The payment facilitator does not mention its pricing details on the website, and its contract terms are a mystery. However, it actively promotes its low processing fee and a dual-price program. Gathered from Paynada Credit Card Processing reviews, here is what merchants should expect in terms of rates and agreement;
Contract Length
A standard Paynada agreement binds merchants to a three-year term. Depending on a company’s type, processing history, and size, the provider also offers month-to-month and seasonal contracts. However, these details are mentioned by a company representative. Clients should verify these claims before committing to the service provider.
Early Cancelation Penalty
The provider promises minor cancelation penalties and charges an ETF of $295. Even though this is quite a standard amount, there is no evidence to back the company’s claims of not forcing any other contract cancelation terms on clients.
Pricing Structure
The provider advertises an interchange plus pricing structure and a dual-pricing model for customers’ convenience, allowing customers to receive a discount on cash payments. It also offers alternate pricing models, including tiered and flat-rate pricing. Paynada promotes its net effective processing cost from 2 to 4% on average.
Processing Fees
Apart from praising its zero-fee processing, the company does not offer insight into its fees and other charges. The official website displays a surcharge and cash discount program offering discounts on products bought with cash. However, this is just a way for merchants to charge an extra 4% on credit card payments. This way, they cover their processing fees by transferring the charges to the customer.
Marketing and Sales
Paynada Credit Card Processing reviews show that the company highly depends on independently hired sales agents to promote its brand. As expected, this sales practice has received its fair share of complaints, as merchants are unhappy with the contradiction between what is said and what is delivered.
The provider also relies on telemarketing and traditional advertisement. However, it fails to provide all the necessary information to potential customers.
Consumer Support
The company has not reserved dedicated consumer support for its clients. A company blog, a support form, and a general contact number are available on the official website. There is also an after-hour phone support number and a generic email address.
Paynada Lawsuits
The provider has faced multiple lawsuits directed against TranzVia. No information is available regarding the fate of these lawsuits. According to Paynada Credit Card Processing reviews, one of the plaintiffs accused the company of violating the Telephone Consumer Protection Act. However, the provider claimed that it was cleared of these allegations.
Reviews and Complaints
Since the provider acquired its recent brand name, few complaints have been associated with it. However, multiple consumer protection websites show numerous complaints about TranzVia, the former company name. Some even accuse the payment facilitator of scamming its clients. Merchants should consider that it is a common practice among service providers to change their brand name to gain a clean slate free from negative criticism.
Unauthorized Deductions
Paynada Credit Card Processing reviews indicate that unwarned charges receive the most complaints. Merchants have complained about being forced to pay for multiple services after account cancelation. The company ignores these complaints by blaming the clients for not canceling one service or another. This is a habit practiced by many unreliable service providers.
Unreliable Sales Representatives
Multiple consumers have doubts regarding Paynada’s sales practices. Some have even claimed that the provider misleads its clients. Hiring the same sales agents by both partner companies is another concerning fact resulting in a rapid increase in complaints by unsatisfied clients. Users have indicated that the services they receive do not match the sales agents’ false promises.
Insufficient Support
To say that the company offers insufficient customer support is an understatement. The website does not enlist any helpline or email support for clients, and there is no live chat facility. Paynada Credit Card Processing reviews hint at merchants depending on a general phone number for their queries and complaints. This does not qualify as a reliable consumer support facility.
Inadequate Information
The payment processor brags about transparency on its website. Yet, it fails to offer any information to its consumers. Users are not entitled to the company’s rates and contract terms and are unaware of the policies and equipment lease conditions. Even the sales representatives are unhelpful in this aspect.
BBB Ranking
Even though Paynada or TranzVia are not accredited with BBB, the latter has an A+ rating on its profile. The review platform shows zero complaints for the company. However, 2 informal negative reviews by consumers were cited, but the provider brushed them away by calling them false.
Account Cancelation Difficulties
Users have complained that the provider ignores their account cancelation requests, continuing to charge monthly fees. Even after the account has been closed, the company refuses to refund the money it keeps deducting from the client’s bank account.
Unethical Practices
Paynada’s team is accused of practicing dishonesty and being rude to the clients. The provider is guilty of sending the wrong equipment to the client and failing to exchange it. Consumers have posted online reviews about the agents ignoring their queries and being harsh. Complainants requesting justification for unauthorized charges wrote about ill-mannered support members unconcerned about the fraud.
Conclusion
As deduced from this Paynada Credit Card Processing review, the company changed its name to free itself from the ill reputation of the former brand. However, this attempt was useless. Paynada failed to revive its clients’ trust as it continued to submerge in old habits. Zero information, sub-par customer service, and unreliable sales practices are severe drawbacks for clients. Moreover, the inability to take consumer complaints seriously and attentively answer clients’ queries are noticeable red flags.
Merchants are encouraged to investigate a payment facilitator’s reputation and previous records before handing out their business.